CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN AFGHANISTAN
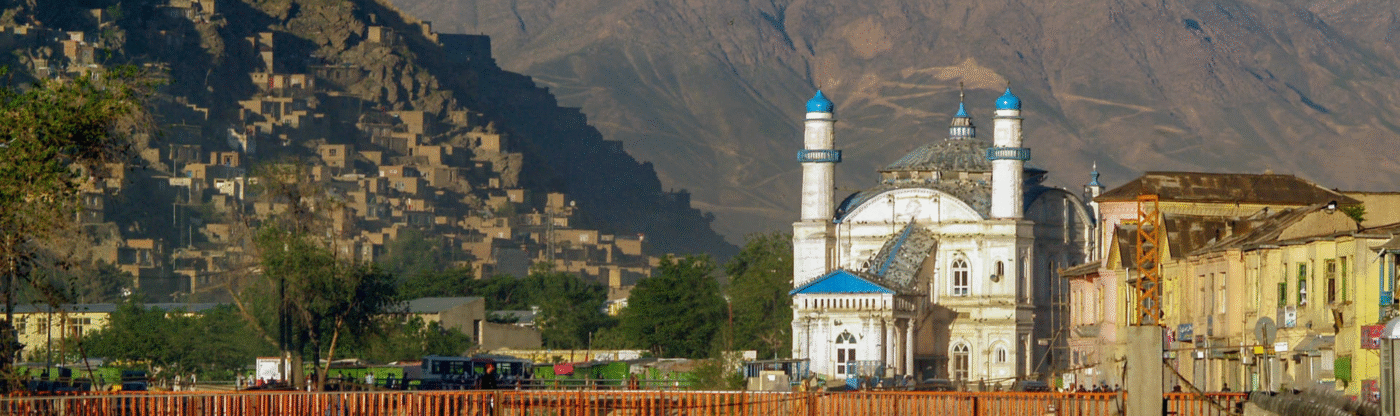
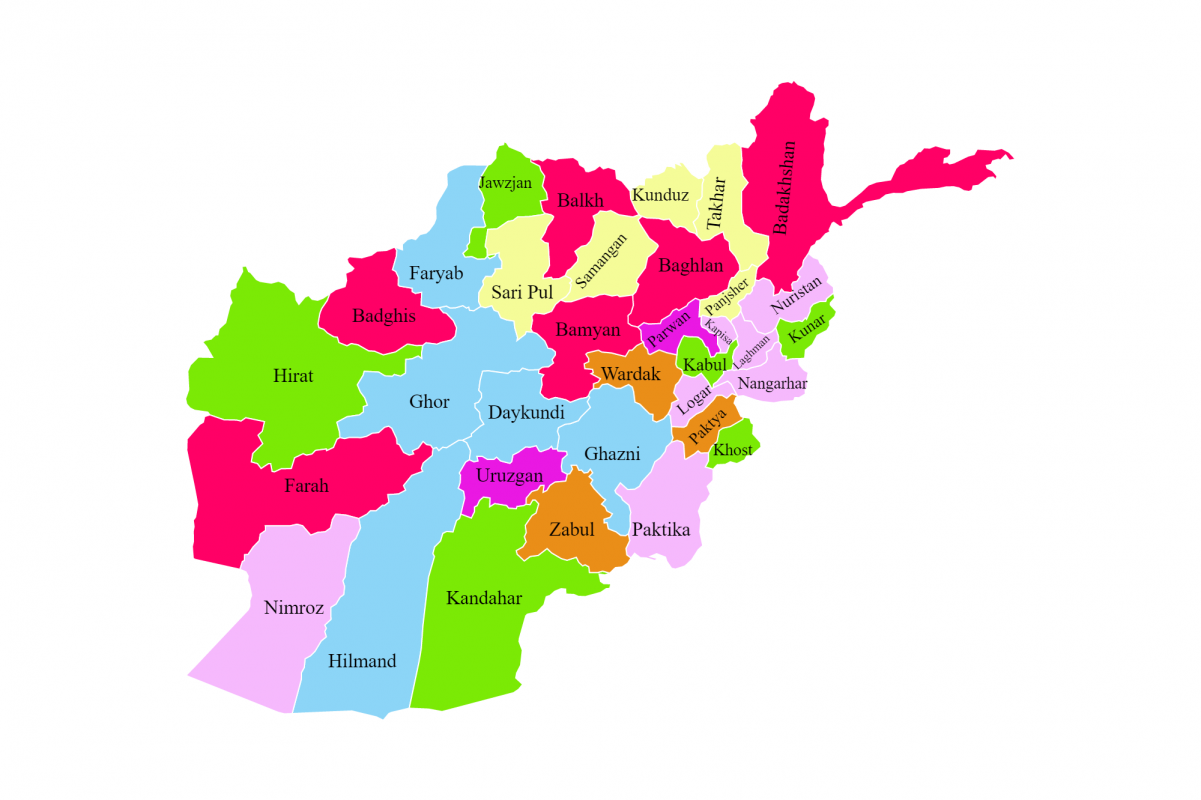
AFGHANISTAN



FLAG

AFGHANISTAN
CAPITAL CITY

KABUL

AFGHAN AFGHANIL
Language

Population

3.98 CRORES
Country
Calling Code

+93
LOCATION:
south Asia
BORDER COUNTRIES:
IRAN
PAKISTAN
TURKMENISTAN
UZBEKISTAN
TAJIKISTAN
ABOUT AFGHANISTAN
Amongst all the countries in Asia, Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in South Asia and Central Asia. It occupies a crucial geographical position at the crossroads of major trade routes, historically connecting the Middle East, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. Afghanistan is renowned for its rich history, diverse cultural heritage, and strategic importance, despite facing significant geopolitical challenges. The capital of Afghanistan is Kabul, which is its largest and most populated city, serving as the country’s primary economic, cultural, and political hub. According to the report of the World Bank, Afghanistan is classified as a Low-Income Country. The currency of Afghanistan is the Afghan Afghani (AFN). As of today’s exchange rates (June 2025), 1 AFN is approximately 0.95 Indian Rupees. The population of Afghanistan is approximately 43 million in 2024. Its neighbouring countries are Pakistan to the south and east, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north, and China to the northeast. The official languages of the country are Pashto and Dari. English is understood and spoken by a segment of the educated population, especially in business and international aid sectors. The vast majority of the population adheres to Islam. Currently, Afghanistan has several international airports, with Hamid Karzai International Airport (KBL) in Kabul being the primary international gateway. Other significant airports include Kandahar International Airport (KDH) and Herat International Airport (HEA), which facilitate domestic and limited international travel. As a landlocked country, Afghanistan does not have seaports; however, it relies on land-based trade routes and dry ports for international commerce.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Afghanistan is 20%. Afghanistan has implemented various tax laws and regulations aimed at promoting domestic and foreign investment, though the political and economic landscape influences their effectiveness. These include provisions for tax exemptions on certain raw materials and machinery imported for manufacturing, as well as incentives for investments in specific strategic sectors. The Afghanistan Investment Facilitation Unit (AIFU) under the Ministry of Industry and Commerce is a key body aimed at promoting and assisting foreign direct investment. Opesh Group of companies will be helping you in completing the Due Diligence process which includes financial planning, registration process, business options, and if required, even helping you find a Rental property for your office.
Establishing a business in Afghanistan involves navigating a complex regulatory environment that has seen some reforms aimed at streamlining processes. Foreign investors planning to start a business in Afghanistan can form various company types, with common structures including Sole Proprietorship, Partnership, and Limited Liability Company (LLC). The LLC structure is often preferred by foreign investors due to its limited liability protection. The legal framework is evolving, and it’s crucial for investors to understand the local regulations and political climate. The Afghanistan Investment Facilitation Unit (AIFU) is the primary government body promoting and assisting foreign direct investment.
In case an investor is planning to establish a business in Afghanistan, Opesh Group will be helping you in taking the right decision for setting up your business and we will also guide you about how to follow the procedure while formulating your company in Afghanistan.
Types of Business which can be started in Afghanistan:
- Agriculture & Agribusiness: As the backbone of the economy, opportunities exist in modernizing agricultural practices, irrigation systems, food processing (e.g., dried fruits, nuts, saffron), and livestock development.
- Mining & Extractive Industries: Afghanistan is rich in untapped mineral resources, including copper, iron, lithium, gold, and rare earth elements. Opportunities exist in responsible extraction, processing, and related infrastructure development.
- Construction & Infrastructure: Given the ongoing need for rebuilding and development, opportunities are present in residential and commercial construction, road networks, and public utilities.
- Telecommunications & IT: The demand for mobile services and internet connectivity continues to grow. Opportunities exist in expanding network infrastructure, digital services, and IT solutions.
- Energy (Hydropower & Renewables): With significant river systems, there’s potential in hydropower projects. Additionally, solar and wind energy projects could address power shortages.
- Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs): Opportunities abound in local manufacturing (e.g., textiles, handicrafts), retail, and various service sectors catering to local needs.
Advantages of Starting Business in Afghanistan:
- Untapped Natural Resources: Vast reserves of minerals offer long-term potential for extractive industries.
- Strategic Regional Location: Historically a trade hub, offering potential for connecting markets in South and Central Asia.
- Young and Growing Population: Provides a potential workforce and a developing consumer market.
- Low Operating Costs: Labor and operational expenses are generally competitive.
- Government Focus (on paper): Efforts to attract foreign investment and rebuild the economy.
Business Opportunities for Indians in Afghanistan: There are business opportunities in Afghanistan for new investors, particularly those with a long-term vision and understanding of the local context. Afghanistan’s resource potential, strategic location, and reconstruction needs present avenues for Indian investors. Indian investors with strengths in mining (especially for iron ore, copper), pharmaceuticals (distribution, local production), agriculture (modern farming techniques, food processing for dried fruits, nuts), construction (infrastructure development), and educational services, can explore avenues for investment and partnerships, especially in the context of humanitarian and development aid projects.
Imports & Exports: Many goods are imported and exported from Afghanistan. Imports and exports business is an ever-growing business in any country; however, you need to do proper R&D before investing in that product which you can import or export. You need to check whether that product is suitable for your target market and how much revenue you will be able to generate from that market.
Major items which are exported from Afghanistan:
- Dried fruits and nuts (e.g., raisins, almonds, pistachios)
- Carpets and rugs
- Medicinal plants and herbs
- Fresh fruits (e.g., pomegranates, grapes, apples)
- Saffron
- Precious and semi-precious stones
- Coal
Major items which are imported in Afghanistan:
- Petroleum products
- Machinery and transport equipment
- Foodstuffs (e.g., wheat flour, sugar, cooking oil)
- Textiles and apparel
- Chemicals
- Building materials
Major items traded between Afghanistan and India (as of recent data):
- Exports from Afghanistan to India: Dried fruits and nuts, fresh fruits, medicinal herbs, saffron, carpets.
- Imports in Afghanistan from India: Pharmaceuticals, tea, machinery, textiles, chemical products, vehicles.
Manufacturing: Manufacturing in Afghanistan is a developing sector, primarily focused on basic consumer goods and agricultural processing. Opportunities exist in food and beverage processing (especially for local agricultural produce), textile manufacturing, construction materials (e.g., cement), and small-scale assembly industries. The sector requires significant investment in infrastructure and technology.
Mining: The mining business in Afghanistan is significant, particularly for untapped mineral wealth. Afghanistan possesses vast reserves of various minerals including copper (Mes Aynak), iron ore (Hajigak), lithium, gold, rare earth elements, chromite, and coal. Opportunities exist in the exploration, extraction, and processing of these minerals, though security and infrastructure remain key challenges.
Major Indian companies which are currently working in Afghanistan: While large-scale Indian manufacturing units may be limited due to the geopolitical situation, Indian interest and presence have historically been in various sectors, often through trade and specific projects.
- Infrastructure & Construction: Indian companies have participated in various infrastructure projects, including road construction (e.g., Zaranj-Delaram highway).
- Pharmaceutical Companies: Indian pharmaceutical products are widely distributed in the Afghan market through local partners.
- IT Services: Some Indian IT and software development companies may provide services or have smaller presences.
- Trading Firms: Various Indian trading houses are involved in the import and export of goods between the two countries, especially for agricultural products.
- Educational Sector: Due to historical ties, some Indian educational institutions or consultants may have collaborations or provide services.
- GDP = $14.5 billion (nominal, 2023 est.)
- GDP Growth = Data is highly volatile and estimates vary widely due to the current political situation.
- Ease of doing business rank = The World Bank’s ‘Doing Business’ report has been discontinued. Afghanistan faces significant challenges in its business environment.
- GDP per Capita = $400 (nominal, 2023 est.)
Thanks for reading this Article. Watch our Video and know more about Afghanistan. For any Business Enquiry Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business.. Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox











