CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN CAMBODIA
CAMBODIA



FLAG

CAMBODIA
CAPITAL CITY
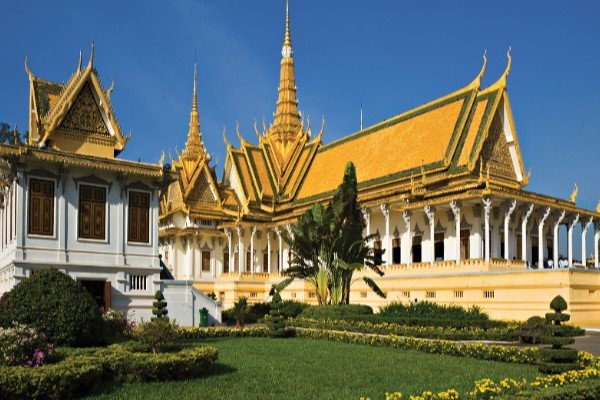

PHNON PENH
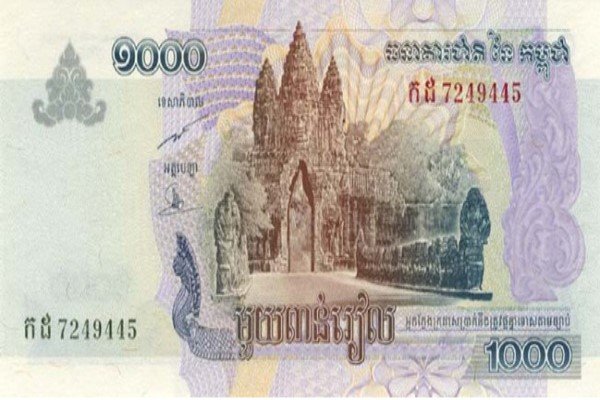

CAMBODIAN RIEL
Language

Population

1.69 CRORES
Country
Calling Code

+855
LOCATION:
ASIA
BORDER COUNTRIES:
THAILAND
LAOS
VIETNAM
THE GULF OF THAILAND
ABOUT CAMBODIA
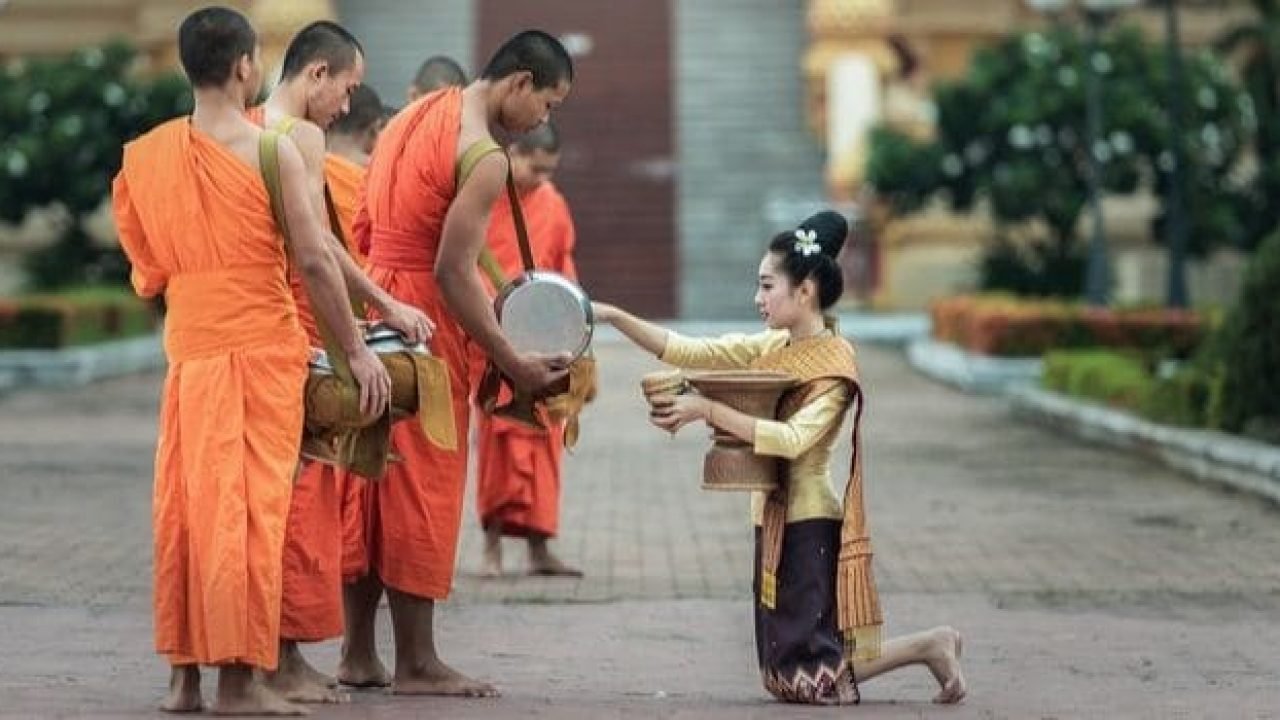
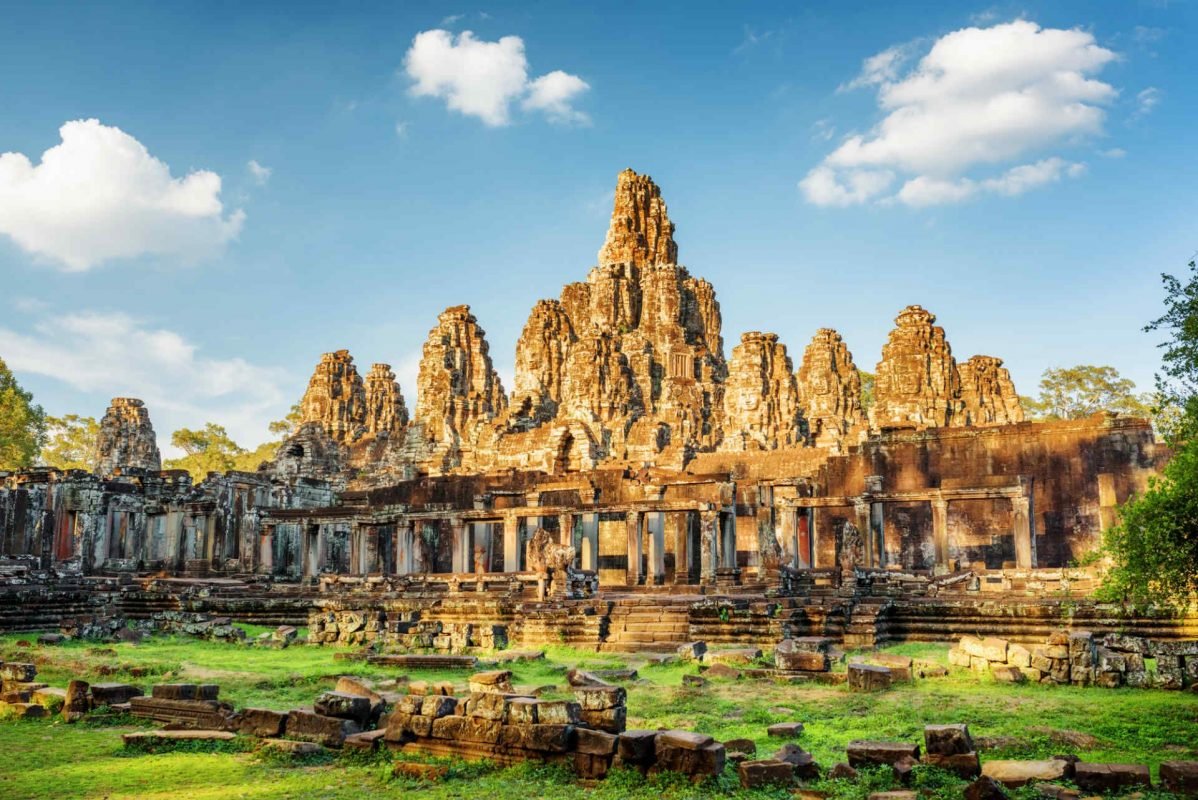
Amongst all the countries in Southeast Asia, Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a nation situated on the Indochinese Peninsula. It is globally renowned for its rich history and ancient heritage, most notably the magnificent Angkor Wat temple complex, a UNESCO World Heritage site. After overcoming a tumultuous past, Cambodia has emerged as a rapidly developing economy, actively integrating into regional and global trade networks. Phnom Penh is the capital and largest city, serving as the country’s political, economic, and cultural center. According to the World Bank, Cambodia is classified as a Lower-Middle Income Economy, with aspirations to reach Upper-Middle Income status by 2030.
The national currency of Cambodia is the Cambodian Riel (KHR), though the US Dollar (USD) is widely circulated and used for most large transactions, particularly in urban areas and for foreign investment. As of today’s exchange rates (June 2025), 1 Cambodian Riel is approximately 0.0204 Indian Rupees (or 1 USD = 83.50 INR, which is more commonly used for significant transactions). The population of Cambodia is estimated at approximately 17.5 million in 2024. Cambodia shares land borders with Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the northeast, and Vietnam to the east. It also has a coastline along the Gulf of Thailand to the southwest. The official language is Khmer. While English is increasingly spoken, especially in tourist areas and business circles, its proficiency varies. The dominant religion is Theravada Buddhism, widely practiced by the Cambodian population. Major international airports include Phnom Penh International Airport (PNH), the newly opened Siem Reap-Angkor International Airport (SAI), and Sihanouk International Airport (KOS). The primary commercial seaport is Sihanoukville Autonomous Port (PAS), which plays a crucial role in facilitating Cambodia’s international trade.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Cambodia is generally 20%. However, specific industries, such as oil and gas or insurance, may have different rates. Cambodia offers attractive investment incentives under its Law on Investment, aimed at attracting Qualified Investment Projects (QIPs), particularly in priority sectors. These incentives are primarily administered by the Council for the Development of Cambodia (CDC) through its Cambodia Investment Board (CIB) and include:
- Tax Holidays: Up to 3 to 9 years of profit tax exemption, depending on the sector and location, plus an additional period of partial exemption.
- Customs Duty Exemption: On imported production equipment, construction materials, and production inputs.
- Special Depreciation: For certain assets.
- Specific Incentives for Special Economic Zones (SEZs): SEZs offer streamlined customs procedures, better infrastructure, and additional tax benefits to encourage export-oriented manufacturing. Opesh Group of companies will be helping you in completing the Due Diligence process which includes financial planning, registration process, business options and if required, even helping you find a Rental property for your office.
Establishing a business in Cambodia has become increasingly streamlined, with the government actively promoting foreign investment through its “open sky” and “open door” policies. Foreign investors can generally establish a Limited Liability Company (LLC), a Branch Office, or a Representative Office. Cambodia’s Law on Investment typically allows for 100% foreign ownership in most sectors, with some specific exceptions (e.g., certain land ownership restrictions, although long-term leases are permitted). The government continues to implement reforms to improve the ease of doing business and enhance its competitiveness as an investment destination.
In case an investor is planning to establish an LLC or a corporate business setup in Cambodia, Opesh Group will be helping you in taking the right decision for setting up your business in Cambodia and we will also guide you about how to follow the procedure while formulating your company in Cambodia.
Types of Business which can be started in Cambodia:
- Garment & Footwear Manufacturing: The cornerstone of Cambodia’s industrial sector, offering opportunities for higher value-added manufacturing, diversification into new products, and sustainable practices.
- Tourism & Hospitality: Leveraging its rich cultural heritage (Angkor Wat), natural beauty, and improving infrastructure, opportunities exist in hotels, resorts, eco-tourism, and related services as the sector recovers.
- Agriculture & Agro-processing: Significant potential in rice, rubber, cassava, pepper, and various fruits, with opportunities for modernization, value addition, and export.
- Infrastructure Development: Demand for investment in roads, railways, ports, airports, energy (including renewables), and digital infrastructure.
- Real Estate & Construction: Driven by urbanization, tourism development, and economic growth, opportunities in residential, commercial, and industrial property.
- Light Manufacturing: Diversification into electronics assembly, auto parts, bicycles, and other light industries.
- Digital Economy: Growing interest in e-commerce, FinTech, digital services, and technology startups, supported by a young population.
Advantages of Starting Business in Cambodia:
- High Economic Growth: One of the fastest-growing economies in Southeast Asia.
- Open for Foreign Investment: Generally allows 100% foreign ownership and offers various incentives.
- Strategic Location: Positioned within the ASEAN bloc, with access to a large regional market.
- Young Workforce: A large and relatively young labor force.
- Preferential Trade Access: Access to major markets through various free trade agreements (e.g., RCEP, bilateral FTAs) and preferential schemes (e.g., GSP).
- US Dollar Usage: Reduces foreign exchange risk for international transactions.
- Untapped Opportunities: Many sectors are still developing, offering less competition for new entrants.
Imports & Exports: Cambodia’s trade profile is heavily influenced by its manufacturing and agricultural sectors.
Major items which are exported from Cambodia:
- Knitted or Crocheted Apparel and Accessories
- Non-Knit Apparel and Accessories
- Footwear
- Travel Goods (bags, luggage)
- Bicycles
- Rubber
- Rice (especially milled rice)
- Cassava
Major items which are imported in Cambodia:
- Fabrics and Textile Raw Materials
- Petroleum Products
- Machinery and Electrical Equipment
- Vehicles
- Construction Materials
- Pharmaceutical Products
- Food and Beverages
Major items traded between Cambodia and India: Trade between Cambodia and India is growing but remains relatively modest compared to Cambodia’s trade with other Asian partners.
- Exports from Cambodia to India: Primarily agricultural products (e.g., rubber, cashew nuts), some textile articles, and wood products.
- Imports in Cambodia from India: Include Pharmaceuticals, Iron & Steel products, Machinery, Vehicles, Cotton, and some food items.
Manufacturing: Manufacturing is a key driver of Cambodia’s economic growth, predominantly focused on labor-intensive, export-oriented industries. The sector is continuously evolving to incorporate higher value-added processes.
- Garment and Footwear Industry: This is the largest manufacturing sector, producing ready-made garments, footwear, and travel goods for major international brands.
- Light Electronics Assembly: Assembly of certain electronic components and parts.
- Food Processing: Processing of agricultural products such as rice, sugar, and various fruits.
- Construction Materials: Production of cement, bricks, and other building materials.
- Bicycles: Cambodia is a significant exporter of bicycles to international markets. The government is encouraging diversification into higher-tech and more complex manufacturing to move up the value chain.
Mining: Cambodia’s mining sector is relatively undeveloped but holds potential, primarily in specific minerals. The country’s economic strength does not heavily rely on large-scale mineral extraction.
- Gold: Gold exploration and some small-scale mining operations are present, with potential for larger commercial ventures.
- Limestone: Used extensively in the cement industry.
- Precious Stones: While historically known for gemstones, large-scale commercial mining is limited.
- Bauxite and Iron Ore: Some deposits exist, but commercial extraction is not extensive.
- Oil and Gas: Exploration for offshore oil and gas reserves is ongoing, with some promising finds. Challenges in the mining sector include regulatory transparency, infrastructure, and environmental concerns.
- GDP = $32.42 billion (nominal, 2024 est. IMF)
- GDP Growth = 6.0% (2024 forecast, IMF); 6.1% (2025 forecast, IMF)
- Ease of doing business rank = The World Bank’s ‘Doing Business’ report has been discontinued. In its last edition (2020), Cambodia ranked 144th out of 190 economies. While challenges persist in areas like contract enforcement and property registration, the government has made efforts to improve business facilitation and reduce bureaucracy, particularly through digital initiatives.
- GDP per Capita = $1,850 (nominal, 2024 est. IMF)
Thanks for reading this Article. Watch our Video and know more about Cambodia. For any Business Enquiry Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business.. Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox