CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN INDONESIA
INDONESIA



FLAG

INDONESIA
CAPITAL CITY

JAKARTA

INDONESIAN RUPIAH
Language

Population

27.66 CRORES
Country
Calling Code

+62
LOCATION:
ASIA
BORDER COUNTRIES:
MALAYSIA
SINGAPORE
THE PHILIPPINESS
AUSTRALIA
THE ANDAMAN
NICOBAR
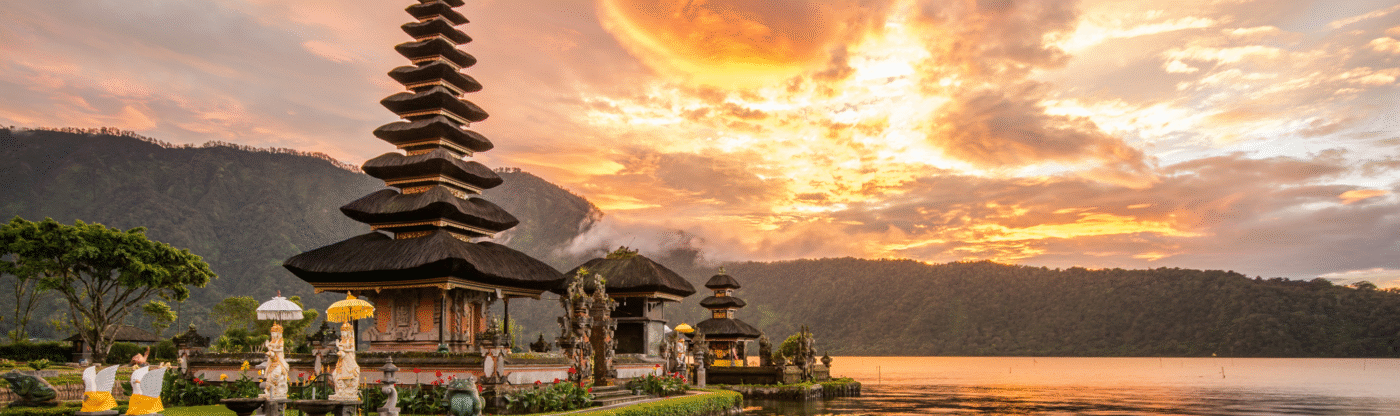
ABOUT INDONESIA
Amongst all the countries in Southeast Asia, Indonesia is the world’s largest archipelagic state and the 4th most populous nation globally. Its strategic location at the crossroads of major shipping lanes and its vast natural resources make it a significant player in the global economy. The current capital is Jakarta, a bustling metropolis and the country’s primary economic and financial center, though the government is actively developing Nusantara as the future capital. According to the World Bank, Indonesia is classified as an Upper-Middle Income Economy and is a member of the G20, reflecting its robust and growing economic standing.
The currency of Indonesia is the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR). As of today’s exchange rates (June 2025), 1 Indian Rupee is approximately 195 – 200 Indonesian Rupiah. The population of Indonesia is estimated at approximately 283.5 million as of 2024. Indonesia shares land borders with Malaysia (on Borneo), Papua New Guinea, and Timor-Leste. It also has maritime borders with Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Australia, and India (via the Andaman Sea). The official and national language is Bahasa Indonesia, a standardized variety of Malay. While Bahasa Indonesia is widely spoken, English proficiency varies, being more common in business and tourist areas, but less so in rural regions. The majority of the Indonesian population practices Islam, with significant minorities practicing Protestantism, Catholicism, Hinduism (predominantly in Bali), Buddhism, and Confucianism. Major international airports include Soekarno-Hatta International Airport in Jakarta (CGK), I Gusti Ngurah Rai International Airport in Denpasar, Bali (DPS), and Juanda International Airport in Surabaya (SUB), providing extensive air connectivity. Indonesia’s vast archipelago means it has numerous commercial seaports, with Tanjung Priok Port in Jakarta, Tanjung Perak Port in Surabaya, and Belawan Port in Medan being among the busiest and most crucial for facilitating both domestic and international trade.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Indonesia is 22%. To attract foreign direct investment and boost economic growth, the Indonesian government offers various investment incentives. These are primarily managed by the Indonesia Investment Coordinating Board (BKPM), now operating under the Ministry of Investment. Incentives include:
- Tax Holidays: Full or partial corporate income tax exemption for a certain period (up to 20 years for large investments in pioneer industries).
- Tax Allowances: Reduced net income for investment (up to 30% over 6 years), accelerated depreciation, lower dividend withholding tax for foreign entities, and extended loss carry-forward.
- Value Added Tax (VAT) Exemptions: For certain imported goods and services, especially in Special Economic Zones (SEZs) and bonded zones.
- Special Economic Zones (SEZs): Offer a range of fiscal incentives (tax holidays, import duty exemptions) and non-fiscal incentives (simplified licensing, relaxed foreign ownership rules) to businesses operating within these designated areas.
- Super Deduction Facilities: For R&D activities (up to 300%) and vocational training.
- Investment in New Capital (IKN Nusantara): Special long-term corporate tax exemptions and various other benefits for businesses investing in the new capital city.
Establishing a business in Indonesia has become significantly more streamlined with the implementation of the Omnibus Law on Job Creation and the Online Single Submission (OSS) system. The most common legal entity for foreign investors is a Foreign Capital Limited Liability Company (PT PMA – Perseroan Terbatas Penanaman Modal Asing). This structure generally allows for 100% foreign ownership in many sectors, though some strategic or sensitive sectors may still have foreign ownership limitations or require local partnerships.
Opesh Group of companies will be helping you in completing the Due Diligence process which includes financial planning, registration process, business options, and if required, even helping you find a rental property for your office. In case an investor is planning to establish a PT PMA or a corporate business setup, Opesh Group will be helping you in taking the right decision for setting up your business in Indonesia and we will also guide you about how to follow the procedure while formulating your company in Indonesia.
Types of Business which can be started in Indonesia:
- Manufacturing: A key driver of Indonesia’s economy, with strong opportunities in automotive, electronics, textiles, food & beverages, chemicals, and the downstream processing of raw materials.
- Digital Economy: Indonesia boasts a massive and rapidly growing digital economy, presenting vast opportunities in e-commerce, fintech, ride-hailing, ed-tech, health-tech, and various startup ventures.
- Infrastructure: Significant government investment in infrastructure projects like roads, ports, airports, railways, and energy infrastructure creates substantial opportunities for construction, engineering, and related services.
- Renewable Energy: With abundant geothermal, solar, and hydro potential, Indonesia is seeking substantial investment to reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and develop its renewable energy sector.
- Mining & Downstream Processing: Rich in minerals like coal, nickel, bauxite, copper, and gold, Indonesia is increasingly focusing on the downstream processing of these resources, particularly for electric vehicle (EV) battery components.
- Agriculture & Agro-processing: As a major global producer of palm oil, rubber, coffee, and various food crops, opportunities exist in improving agricultural productivity, developing agro-processing industries, and expanding fisheries.
- Tourism: A vital sector with immense potential, particularly in Bali and other popular destinations. Opportunities exist in hotel development, tourism infrastructure, eco-tourism, and hospitality services.
Advantages of Starting Business in Indonesia:
- Large Domestic Market: With over 280 million people, Indonesia offers a massive consumer base and a growing middle class.
- Abundant Natural Resources: Rich in minerals, energy sources, and agricultural land, providing raw materials for various industries.
- Strategic Location: Its position in Southeast Asia provides access to regional markets and major global shipping lanes.
- Demographic Dividend: A young and growing workforce provides ample human resources for various industries.
- Government Support for Investment: The government actively promotes foreign investment through favorable policies, incentives, and a dedicated investment board (BKPM).
- Membership in ASEAN & G20: Facilitates regional trade integration and positions Indonesia as a key player in the global economy.
- Improving Ease of Doing Business: Continuous reforms aimed at simplifying business registration and operations.
Imports & Exports: Indonesia is a significant global trader, heavily reliant on its natural resources and manufacturing capabilities.
Major items which are exported from Indonesia:
- Mineral Fuels (e.g., coal, crude petroleum, natural gas)
- Animal & Vegetable Fats and Oils (primarily palm oil and its derivatives)
- Iron and Steel (especially nickel-based products)
- Electrical Machinery and Equipment
- Rubber and Rubber Articles
- Vehicles and Automotive Parts
- Footwear and Textiles
Major items which are imported in Indonesia:
- Machinery and Mechanical Appliances
- Electrical Machinery and Equipment
- Mineral Fuels and Oils (refined petroleum products)
- Plastics and Plastic Articles
- Iron and Steel Products
- Chemical Products
- Cereals (e.g., wheat, rice)
Business Opportunities for Indians in Indonesia: There are excellent and growing business opportunities for Indian investors in Indonesia, driven by strong bilateral relations and complementary economic needs. India is a significant trading partner for Indonesia.
- Manufacturing: Opportunities exist in setting up manufacturing plants, particularly in automotive components, electronics, textiles, and pharmaceutical production, leveraging Indonesia’s large labor force and domestic market.
- Mining & Energy: Continued opportunities in coal mining and trading, palm oil plantations, and exploring investments in nickel processing for EV batteries.
- Digital Economy: Significant potential for Indian IT companies, e-commerce players, and fintech startups to tap into Indonesia’s burgeoning digital market.
- Infrastructure Development: Indian companies can participate in various infrastructure projects, including port development, road construction, and power generation.
- Pharmaceuticals: India’s strong pharmaceutical sector can find opportunities in manufacturing, distribution, and research collaboration in Indonesia.
- Agro-processing: Investment in processing agricultural products, leveraging Indonesia’s raw materials.
Major Indian companies which are currently working in Indonesia: Several prominent Indian companies have established a significant presence in Indonesia, particularly in the energy, manufacturing, and IT sectors.
-
Tata Power: Active in the energy sector, particularly in coal mining.
-
Adani Group: Involved in the energy and mining sectors, including coal.
-
TCS, Tech Mahindra, HCLTech: Major Indian IT service providers with operations serving the growing digital economy.
-
Godrej Consumer Products: Has a significant presence in the consumer goods market.
-
Jubilant Bhartia Group (Jubilant Agri and Consumer Products Limited): Involved in agricultural and consumer products.
-
Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL): Has been involved in power plant projects.
-
Various Indian pharmaceutical companies have a strong presence through exports and distribution.
-
GDP = $1.429 trillion (nominal, 2025 est. IMF)
-
GDP Growth = 5.03% (2024 est. IMF); ~5.0% (2025 forecast by various sources)
-
Ease of doing business rank = The World Bank’s ‘Doing Business’ report has been discontinued. Indonesia has made significant reforms to improve its business environment, indicated by its pre-suspension ranking and ongoing government efforts to attract investment through policies like the Omnibus Law.
-
GDP per Capita = $5,026 (nominal, 2025 est. IMF)
Thanks for reading this Article. Watch our Video and know more about Indonesia. For any Business Enquiry Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business.. Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox











