CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN NEPAL
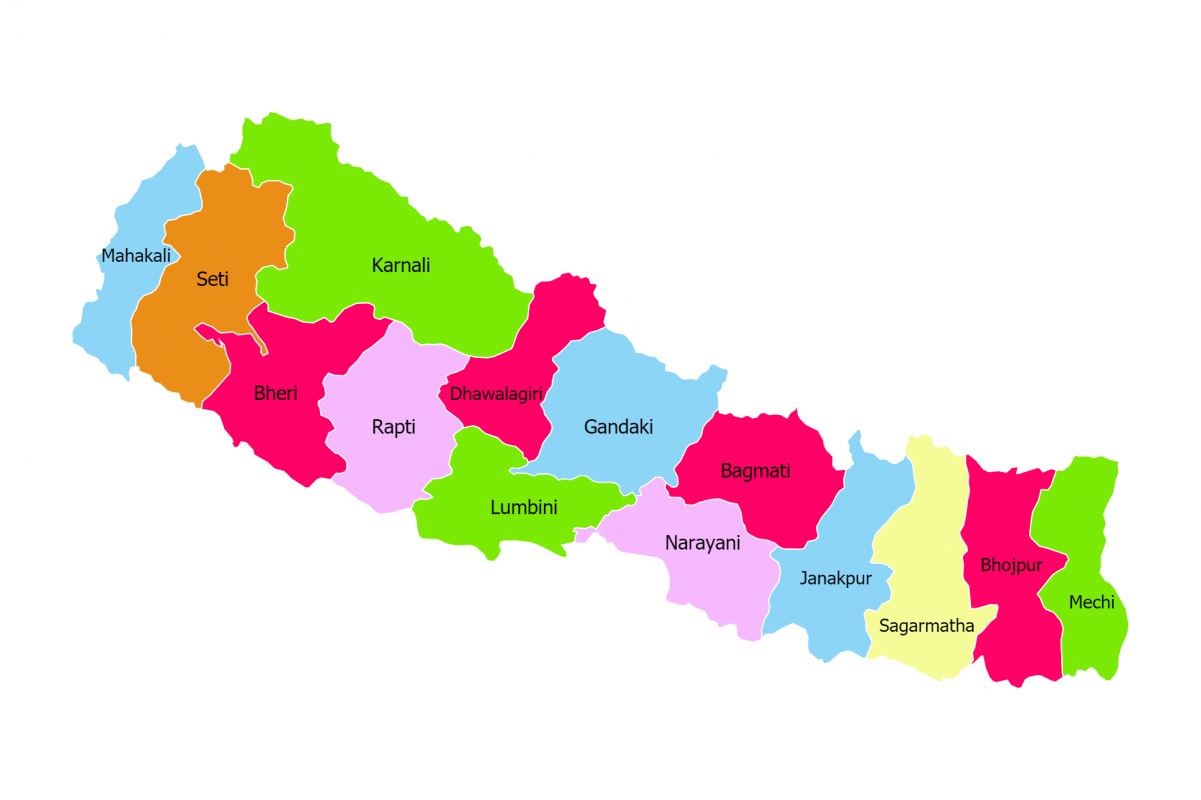
NEPAL



FLAG

NEPAL
CAPITAL CITY
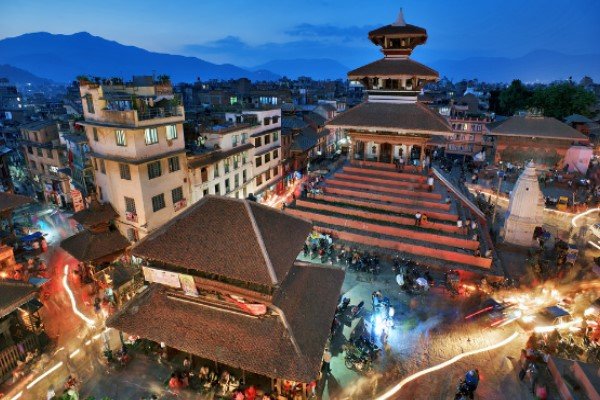

KATHMANDU
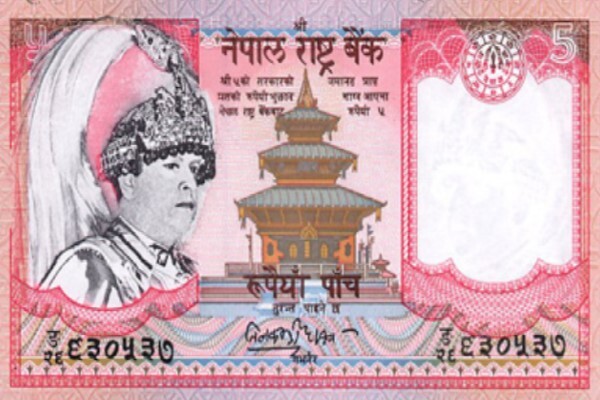

NEPALESE RUPEE
Language

Population

2.97 CRORES
Country
Calling Code

+977
LOCATION:
SOUTH ASIA
BORDER COUNTRIES:
CHINA
INDIA
ABOUT NEPAL
Amongst all the countries in South Asia, Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country primarily situated in the Himalayas, but also encompassing parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It is globally recognized as the birthplace of Lord Buddha, home to Mount Everest (the world’s highest peak), and boasts a rich tapestry of ancient kingdoms, diverse cultures, and unique spiritual heritage. Having transitioned from a monarchy to a federal democratic republic, Nepal is now focusing on economic development and poverty reduction. The capital of Nepal is Kathmandu, which is its largest and most populous city, serving as the country’s main administrative, economic, and cultural hub. According to the World Bank, Nepal is currently classified as a Lower-Middle Income Economy, actively working towards graduating from its Least Developed Country (LDC) status.
The currency of Nepal is the Nepalese Rupee (NPR), which is pegged to the Indian Rupee (INR) at a fixed exchange rate. As of today’s date (June 2025), 1 Indian Rupee is approximately 1.60 Nepalese Rupees (or 1 NPR = 0.625 INR). The population of Nepal is estimated at approximately 29.6 million in 2024. Its neighboring countries are India to the south, east, and west, and the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north. Being landlocked, Nepal relies on India for transit access to the sea, primarily through the ports of Kolkata and Haldia. The official language of the country is Nepali. English is widely spoken and understood, especially in urban areas, tourism, and business sectors. Hinduism is the dominant religion, with a significant Buddhist population and smaller communities of other faiths, coexisting harmoniously. Nepal has three international airports: Tribhuvan International Airport (KTM) in Kathmandu, Gautam Buddha International Airport (BWA) in Bhairahawa (near Lumbini), and Pokhara International Airport (PKR). As a landlocked country, Nepal does not have its own seaports but utilizes Indian seaports like Kolkata and Haldia for international trade via overland routes.
The standard corporate income tax rate in Nepal is 25% for most industries. However, certain sectors like banks, financial institutions, insurance companies, and petroleum businesses are taxed at 30%. “Special industries,” which often include manufacturing and infrastructure projects, may enjoy a lower rate of 20%. To attract foreign direct investment (FDI), Nepal offers various incentives. These typically include income tax holidays (especially for industries in Special Economic Zones – SEZs or those prioritizing exports, hydropower, or specific manufacturing sectors), customs duty exemptions on essential machinery and raw materials, and provisions for easy repatriation of profits and dividends. Industries established within SEZs can enjoy a 100% income tax holiday for the first 5-10 years, followed by a 50% exemption for subsequent years, depending on the SEZ location. The Investment Board Nepal (IBN) is the primary government body responsible for promoting, facilitating, and approving large-scale foreign investments, especially projects exceeding certain thresholds (e.g., NPR 6 billion or hydropower projects above 200 MW). The Department of Industry (DOI) handles smaller investments. Opesh Group of companies will be helping you in completing the Due Diligence process which includes financial planning, registration process, business options, and if required, even helping you find a Rental property for your office.
Establishing a business in Nepal involves navigating regulations aimed at improving the investment climate. The government has taken steps to simplify procedures, such as reducing the minimum foreign investment threshold to NPR 20 million (approx. USD 150,000). For foreign investors, common business structures include establishing a Private Limited Company (Pvt. Ltd.), which is the most popular, or a Public Limited Company. A Branch Office of a foreign company is also an option, particularly for specific projects. Generally, 100% foreign ownership is allowed in most sectors, provided the industry is not on the “negative list” (e.g., certain small-scale industries, defense, primary agriculture). While the process has been streamlined, investors may still encounter bureaucratic complexities and infrastructure challenges.
In case an investor is planning to establish a Private Limited Company or a corporate business setup in Nepal, Opesh Group will be helping you in taking the right decision for setting up your business in Nepal and we will also guide you about how to follow the procedure while formulating your company in Nepal.
Types of Business which can be started in Nepal:
- Hydropower: Nepal possesses immense hydropower potential, with only a fraction currently harnessed. This is a top priority sector for both domestic consumption and export.
- Tourism & Hospitality: Leveraging its natural beauty (mountains, trekking, wildlife) and cultural heritage (Lumbini, ancient temples), opportunities exist in hotels, resorts, adventure tourism, and eco-tourism.
- Agriculture & Agro-Processing: Modernizing agricultural practices, developing commercial farming, and processing high-value products (e.g., organic produce, tea, coffee, herbs) for domestic and export markets.
- Manufacturing: Small to medium-scale manufacturing focusing on import substitution and export-oriented products, especially in textiles, garments, cement, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials.
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) & IT-Enabled Services: Given a growing young population and relatively lower labor costs, opportunities exist in software development, BPO, and IT services.
- Infrastructure Development: Significant need for development in roads, railways, airports, and urban infrastructure.
Advantages of Starting Business in Nepal:
- Abundant Hydropower Potential: A major source of clean energy and export revenue.
- Growing Tourism Sector: Unique natural and cultural attractions drawing increasing numbers of visitors.
- Strategic Location: Proximity to two large markets (India and China).
- Preferential Trade Access: Benefits from various regional and international trade agreements.
- Young Workforce: A large and increasingly literate youth population.
- Investment Incentives: Government offers tax breaks and other benefits to attract FDI.
- Fixed Exchange Rate: Peg to Indian Rupee provides currency stability for trade with India.
Business Opportunities for Indians in Nepal: There are significant business opportunities in Nepal for Indian investors, driven by geographical proximity, cultural ties, and the fixed exchange rate. India is Nepal’s largest trading partner and a major source of FDI. Indian investors can particularly explore avenues in:
- Hydropower Development: Direct investment in power generation projects and cross-border electricity trade.
- Infrastructure: Involvement in road, railway, airport, and other connectivity projects, often with Indian government support.
- Banking & Financial Services: Presence of major Indian banks and opportunities in digital payments and financial technology.
- Manufacturing: Setting up manufacturing units for consumer goods, construction materials, and pharmaceuticals, leveraging Nepal’s preferential access to the Indian market for certain products.
- Telecommunications: Continued investment in mobile network expansion and internet services.
- Tourism: Development of hotels, resorts, and tourism infrastructure, especially for pilgrims and adventure tourists.
- Healthcare & Education: Establishing hospitals, medical colleges, and educational institutions.
Imports & Exports: Nepal’s trade balance is heavily skewed towards imports. Efforts are underway to boost exports and reduce the trade deficit.
Major items which are exported from Nepal:
- Palm Oil, Soyabean Oil (often re-exported after processing imported crude oil)
- Cardamom, Tea, and other agricultural products
- Carpets and other textile products
- Iron and Steel products
- Garments
Major items which are imported in Nepal:
- Petroleum products (diesel, petrol, LPG)
- Machinery and equipment
- Vehicles
- Gold
- Electrical goods
- Medicines
- Food products
Major items traded between Nepal and India (as of 2023-2025 data):
- Exports from Nepal to India: Palm oil, soyabean oil, cardamom, pulses, textiles, iron and steel products. India is Nepal’s primary export destination.
- Imports in Nepal from India: Petroleum products, machinery and equipment, vehicles, food grains, consumer goods, pharmaceuticals, and electricity. India is Nepal’s dominant source of imports.
Manufacturing: Nepal’s manufacturing sector is relatively small but growing, focusing on industries that cater to domestic demand and utilize local resources. Key manufacturing sub-sectors include food and beverages, textiles and garments, cement, pharmaceuticals, and construction materials. The government is promoting industrial estates and Special Economic Zones to boost manufacturing output and exports.
Mining: The mining sector in Nepal is largely underdeveloped despite potential reserves. Limestone is the most commercially exploited mineral, primarily for cement production. Other identified mineral resources include coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, gold, and uranium, but their commercial viability and extraction remain limited. Efforts are underway to attract investment for systematic exploration and development of these resources.
- GDP = $43.67 billion (nominal, 2024 est. IMF)
- GDP Growth = 3.9% (FY24 est.), 4.5% (FY25 forecast – World Bank); 3.1% (2024 est.), 4.0% (2025 forecast – IMF)
- Ease of doing business rank = The World Bank’s ‘Doing Business’ report has been discontinued. In its last edition (2020), Nepal ranked 94th globally, and 3rd in South Asia, reflecting significant improvements in areas like getting credit and construction permits. However, challenges persist in areas like paying taxes and starting a business.
- GDP per Capita = $1,460 (nominal, 2025 est. IMF)
Thanks for reading this Article. Watch our Video and know more about Nepal. For any Business Enquiry Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business.. Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox










