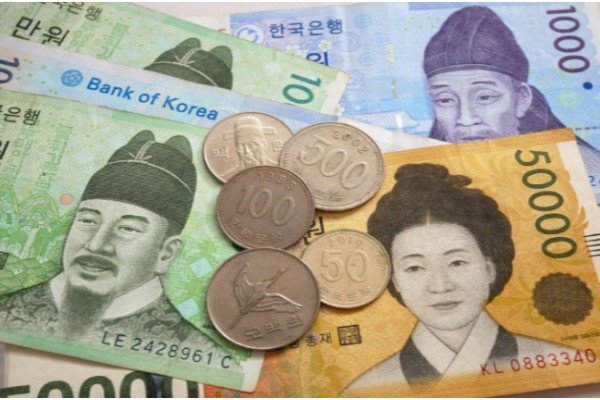
CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN SOUTH KOREA
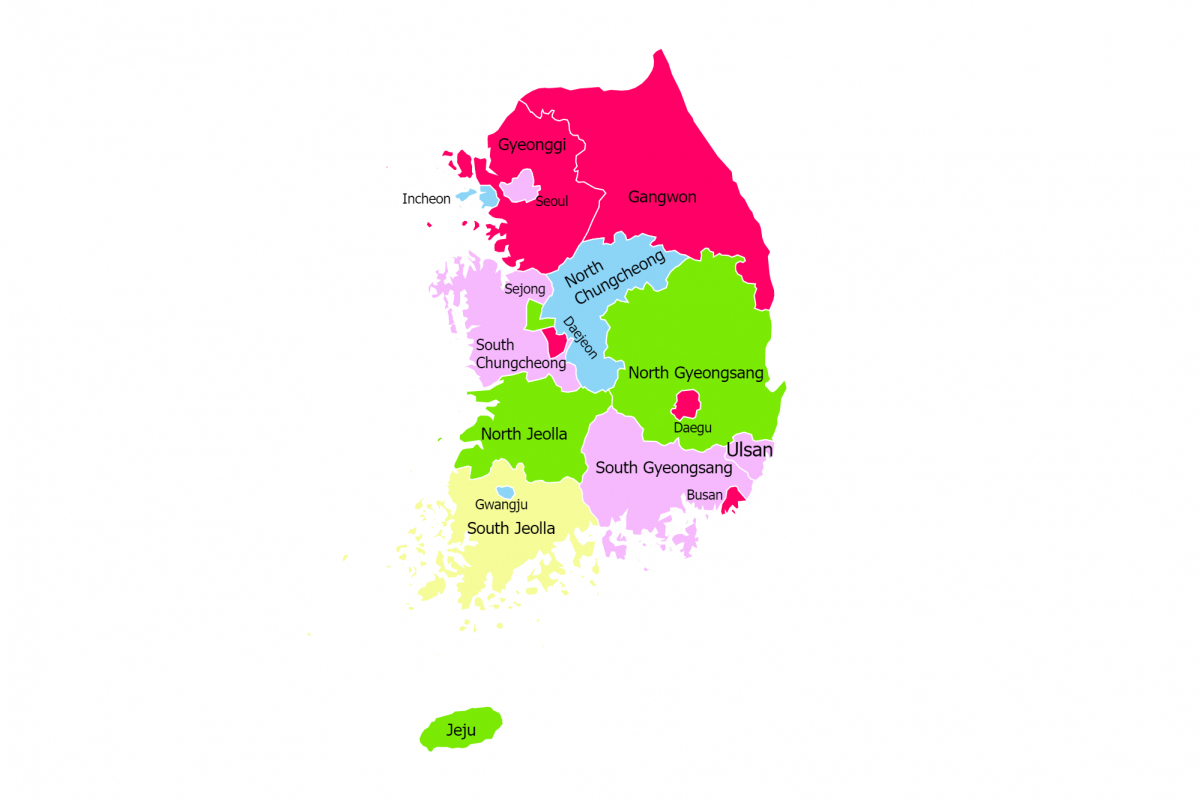
SOUTH KOREA



FLAG

SOUTH KOREA
CAPITAL CITY
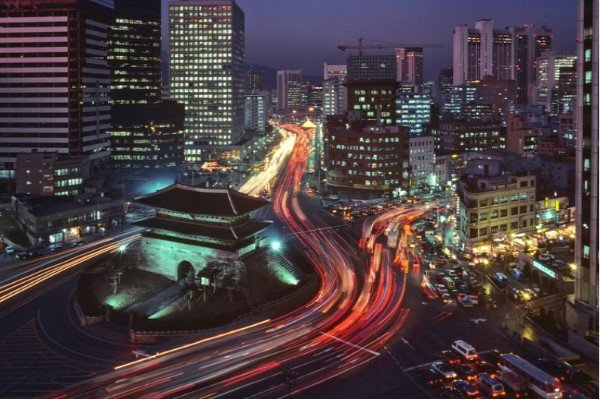

SEOUL

ALGERIAN DINAR
Language

Population

5.13 CRORES
Country
Calling Code

+82
LOCATION:
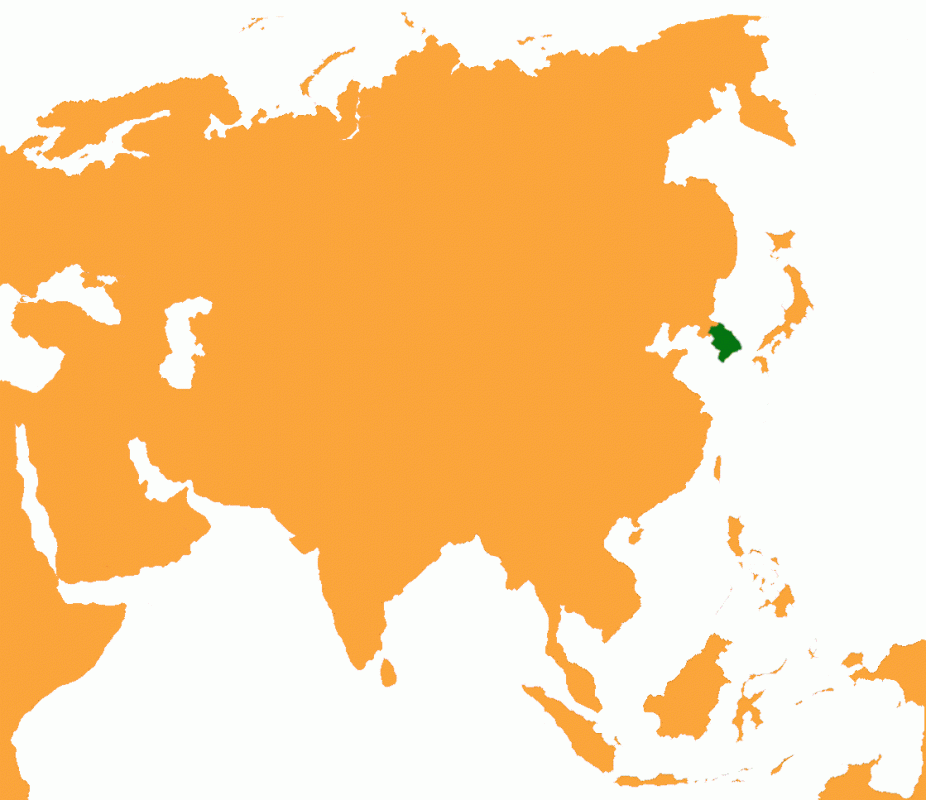
EAST ASIA
BORDER COUNTRIES:
NORTH KOREA
CHINA
JAPAN
ABOUT SOUTH KOREA
Amongst all the countries in East Asia, South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea, occupies the southern half of the Korean Peninsula. It is a highly developed country renowned for its incredible economic transformation, often referred to as the “Miracle on the Han River,” which saw it rise from post-war devastation to become a global leader in technology, automotive, shipbuilding, and popular culture (K-pop, K-drama). Seoul is the capital and largest city, serving as the nation’s political, economic, and cultural heart, home to major global corporations and a vibrant urban landscape. According to the World Bank, South Korea is classified as a High-Income Economy and by the IMF as an advanced economy.
The currency of South Korea is the South Korean Won (KRW). As of today’s exchange rates (June 2025), 1 South Korean Won is approximately 0.062 Indian Rupees. The population of South Korea is estimated at approximately 51.7 million in 2024. South Korea shares a heavily fortified land border with North Korea to its north. It has maritime borders with Japan to the east across the East Sea (Sea of Japan) and the Korea Strait, and with China to the west across the Yellow Sea. The official language is Korean, with its unique alphabet, Hangeul. While English proficiency varies, it is commonly taught and used in business and international contexts, especially among younger generations. South Korea is a diverse society in terms of religion; a significant portion of the population is non-religious, with large Christian and Buddhist communities. Major international airports include Incheon International Airport (ICN) in Seoul, Gimpo International Airport (GMP) also in Seoul, and Jeju International Airport (CJU). Its key commercial seaports are Busan Port (one of the world’s busiest container ports), Incheon Port, Ulsan Port, and Gwangyang Port, which are vital for its export-oriented economy.
The standard corporate income tax rate in South Korea is progressive, with a maximum rate of 25% for taxable income exceeding KRW 200 billion. Lower rates apply to smaller income brackets (e.g., 10% for income up to KRW 200 million, 20% for income between KRW 200 million and KRW 20 billion). Additionally, a local income tax of 10% of the corporate income tax is levied. Invest Korea, a division of KOTRA (Korea Trade-Investment Promotion Agency), is the primary government agency promoting foreign direct investment. South Korea offers various investment incentives under the Foreign Investment Promotion Act (FIPA), including:
- Tax Reductions/Exemptions: For foreign-invested companies operating in Free Economic Zones (FEZs), Foreign Investment Zones (FIZs), or engaging in high-tech industries and specific service sectors. This can include reductions or exemptions on corporate income tax, customs duties, acquisition tax, and property tax.
- Cash Grants: For significant foreign investments that meet specific criteria related to job creation, technology transfer, or regional development.
- Location Support: Subsidies for land purchase or rental, and support for construction costs in designated foreign investment areas.
- R&D Support: Various incentives and support for foreign companies establishing R&D centers. Opesh Group of companies will be helping you in completing the Due Diligence process which includes financial planning, registration process, business options and if required, even helping you find a Rental property for your office.
Establishing a business in South Korea is considered relatively straightforward due to a well-developed regulatory framework and government support for foreign investors. The Foreign Investment Promotion Act (FIPA) governs foreign direct investment, generally allowing 100% foreign ownership in most business sectors. Common company types that foreign investors can establish include a Stock Company (Jusik Hoesa), a Limited Company (Yuhan Hoesa), a Limited Liability Company (Yuhan Chaegim Hoesa), or a Branch Office. South Korea consistently ranks high in global ease of doing business indices, reflecting its transparent and efficient administrative procedures.
In case an investor is planning to establish an LLC or a corporate business setup in South Korea, Opesh Group will be helping you in taking the right decision for setting up your business in South Korea and we will also guide you about how to follow the procedure while formulating your company in South Korea.
Types of Business which can be started in South Korea:
- Semiconductors & Displays: A global leader in memory chips, logic chips, and advanced display technologies.
- Automotive & Future Mobility: Investment in electric vehicles (EVs), autonomous driving, smart mobility solutions, and components.
- Batteries: Focus on advanced battery technologies for EVs and energy storage systems.
- Bio-health: Strong growth in pharmaceuticals, biopharmaceuticals, medical devices, and digital healthcare.
- AI & Digital Technologies: Development in artificial intelligence, 5G/6G, IoT, Big Data, cloud computing, and cybersecurity.
- Robotics: Advanced manufacturing, service robots, and industrial automation.
- Renewable Energy & Hydrogen Economy: Significant government push for solar, wind, and hydrogen fuel cell technologies.
- Content & Culture: Leveraging the global success of K-pop, K-drama, gaming, and animation.
Advantages of Starting Business in South Korea:
- Innovation Powerhouse: A global leader in R&D, technology adoption, and digital transformation.
- Highly Skilled Workforce: Educated, innovative, and driven talent pool, especially in STEM fields.
- Strong Economic Foundation: Robust, diversified economy with large domestic market and significant export capabilities.
- World-Class Infrastructure: Advanced digital connectivity, transportation networks, and smart cities.
- Government Support: Comprehensive incentives and support for foreign direct investment through Invest Korea and other agencies.
- Strategic Location: Gateway to major East Asian markets (China, Japan).
- IP Protection: Strong legal framework for intellectual property rights.
Imports & Exports: South Korea’s economy is highly export-oriented, driven by its advanced manufacturing capabilities, and heavily reliant on imported raw materials.
Major items which are exported from South Korea:
- Integrated Circuits (Semiconductors)
- Automobiles and Parts
- Petroleum Products
- Flat Display Panels
- Ships and Offshore Structures
- Wireless Communication Equipment
- Chemical Products
Major items which are imported in South Korea:
- Crude Petroleum
- Electronic Integrated Circuits
- Natural Gas (LNG)
- Coal
- Machinery
- Electrical Equipment
- Iron and Steel
- Organic Chemicals
Major items traded between South Korea and India:
- Exports from South Korea to India: Primarily Electronic goods (semiconductors, displays), Automotive parts, Petrochemicals, Steel products, and Machinery.
- Imports in South Korea from India: Mineral fuels (including refined petroleum products), Chemicals, Iron and Steel, Agricultural products (e.g., cotton, food grains), and some consumer goods. Indian IT services are also growing in demand.
Manufacturing: Manufacturing is the backbone of South Korea’s economy, characterized by high technology, large-scale production, and global competitiveness. Key manufacturing sectors include:
- Semiconductors: Dominates global memory chip production and is a growing player in logic chips.
- Automotive: Home to global giants like Hyundai and Kia, producing a wide range of vehicles, including a strong focus on EVs.
- Shipbuilding: One of the world’s leading shipbuilders, specializing in high-value vessels and LNG carriers.
- Electronics: Production of consumer electronics (smartphones, TVs), home appliances, and various electronic components.
- Chemicals: Extensive production of petrochemicals, plastics, and advanced materials.
- Steel: Major global steel producers like POSCO.
- Batteries: Significant investment and production capacity for EV batteries. South Korea consistently invests in R&D and automation to maintain its technological edge in manufacturing.
Mining: South Korea is poor in natural mineral resources and is heavily dependent on imports for most raw materials required by its vast manufacturing industries. The mining sector is therefore very small.
- Coal: Limited anthracite coal mining still exists, but production has significantly declined due to environmental concerns and economic viability.
- Limestone: Mined primarily for cement production and other construction materials.
- Small deposits of some non-metallic minerals. The country’s economic strength lies in its human capital, technological innovation, and manufacturing prowess, rather than its natural resource extraction.
- GDP = $1.950 trillion (nominal, 2025 est. IMF)
- GDP Growth = 2.3% (2024 forecast, IMF); 2.1% (2025 forecast, IMF)
- Ease of doing business rank = The World Bank’s ‘Doing Business’ report has been discontinued. In its last edition (2020), South Korea consistently ranked among the top 5 global economies for ease of doing business, reflecting its efficient regulatory environment, particularly in areas like enforcing contracts, getting electricity, and protecting minority investors.
- GDP per Capita = $37,672 (nominal, 2025 est. IMF)
Thanks for reading this Article. Watch our Video and know more about South Korea. For any Business Enquiry Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business.. Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox











