CURRENCY
BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES IN THAILAND
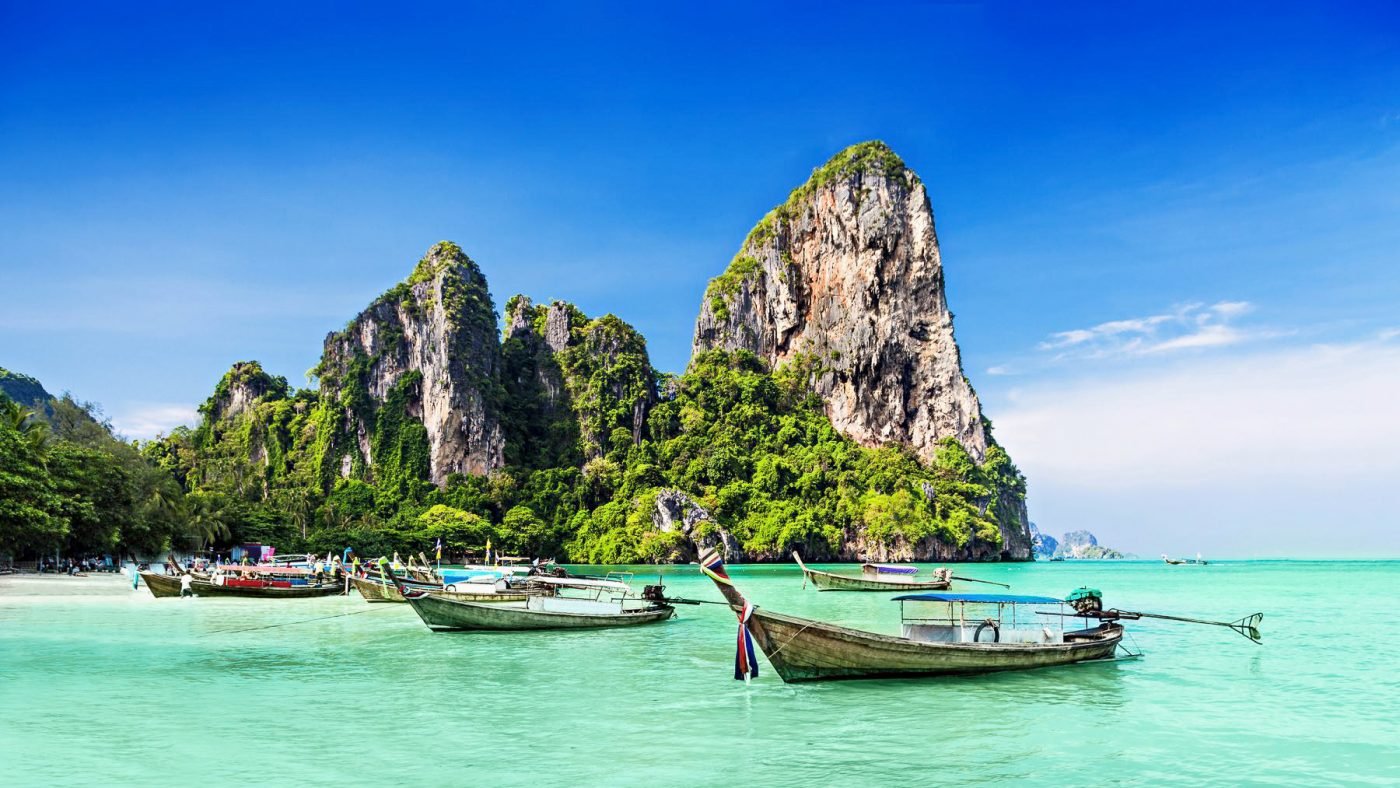
THAILAND



FLAG

BANGKOK
CAPITAL CITY

BANGKOK
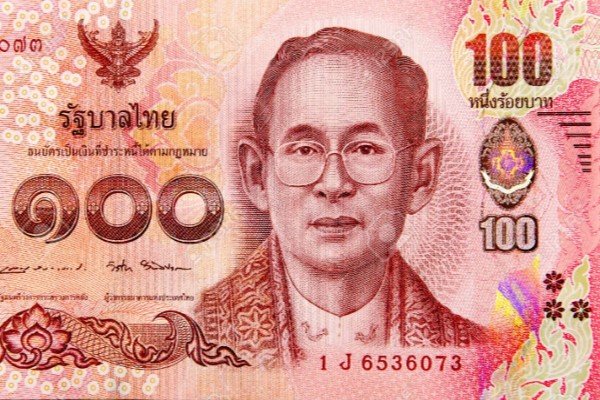

THAI BAHT
Language

Population

69.99 LAKHS
Country
Calling Code

+66
LOCATION:
aSIA
BORDER COUNTRIES:
CAMBODIA
LAOS
MALAYSIA
MYANMAR
THE  MONEY SHOW SEASON 2.0
MONEY SHOW SEASON 2.0
Mining and Infrastructure Business in Algeria
Facebook live 7.00 Pm Today.
Join Millionaire Program and change everything in life and Business..
Call/ WhatsApp +91- 8094607111.
GDP= $579.00 billion
GDP Growth= 3.9%
Ease of doing business rank= 21
GDP per Capita= $6,600
MOST RECENT VIDEOS
SIGN UP TODAY
Get our exclusive content and offers in your inbox










